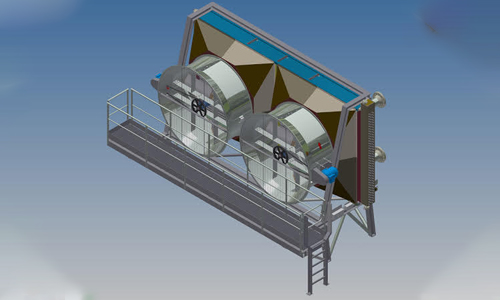


Air-cooled heat exchangers (ACHEs) are used in chemical, petrochemical, and power generation industries, where they transfer heat from process fluids to surrounding air. They employ finned tubes to enhance the heat transfer surface area significantly, thus being very effective in applications where the air-side heat transfer coefficient is low. Tube bundles are blown across by ambient air using fans, which can be horizontally or vertically oriented depending on the design.
ACHEs are best suited for areas with scarce water resources, expensive water treatment, or stringent environmental discharge standards. While their initial capital investment is greater than that of water-cooled systems, ACHEs have lower operating and maintenance expenses, obviating issues associated with water fouling, corrosion, and leakage.
They are extensively utilized for cooling and condensing in process plants. The main components are tube bundles, support structures, fans, plenum chambers, and finned tubes, each of them being tailored to fulfill a particular operational need.